Defining the Cloud computing and its advantages
The cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services, including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics
Cloud computing has emerged as a transformative technology that has revolutionized the way we store, access, and manage data and applications.
In this blog post, we'll explore the concept of cloud computing and delve into its myriad advantages that have made it an indispensable tool in our increasingly connected world.
What is Cloud Computing?
At its core, cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services ? including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence ? over the internet.
Unlike traditional computing where data and applications are stored on a local server or a personal computer, cloud computing uses remote servers hosted in data centers to process and store information.
Users can access these services and resources on-demand from virtually anywhere with an internet connection.
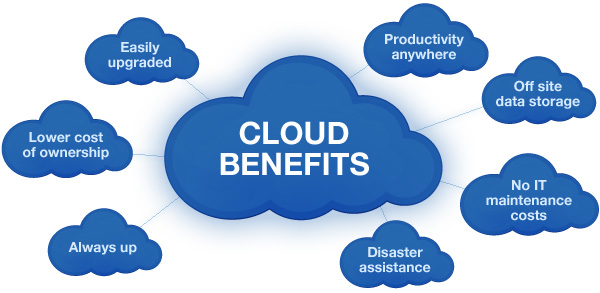
Advantages of Cloud Computing
- Cost Efficiency
One of the most compelling advantages of cloud computing is its cost-effectiveness. Traditional IT infrastructure requires substantial upfront capital investment in hardware, software, and maintenance. In contrast, cloud computing operates on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing businesses and individuals to scale resources up or down as needed. This flexibility eliminates the need for excessive hardware purchases and reduces operational and maintenance costs.
- Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud computing offers unparalleled scalability and flexibility. Whether you're a small startup or a large enterprise, cloud services can easily adapt to your changing needs. You can quickly provision additional resources during high-demand periods and scale down during quieter times, all with minimal effort and cost. This agility empowers businesses to respond to market fluctuations and innovation opportunities rapidly.
- Accessibility
The cloud is accessible from virtually anywhere with an internet connection. This means you can access your data and applications on a variety of devices, including smartphones, tablets, laptops, and desktop computers. This level of accessibility fosters remote work, collaboration, and productivity, especially in today's remote work culture.
- Reliability and Redundancy
Leading cloud providers invest heavily in infrastructure redundancy and security measures. This results in exceptional reliability and uptime for cloud services. With data centers distributed worldwide, cloud providers can ensure your data is accessible even in the face of hardware failures or natural disasters.
- Security
Cloud providers take security seriously. They employ teams of experts dedicated to safeguarding data and infrastructure. Cloud services often include advanced security features like encryption, identity and access management, and threat detection. For many organizations, storing data in the cloud can be more secure than maintaining it on-premises, where security measures might be lacking.
- Automatic Updates and Maintenance
Cloud providers handle the tedious task of software updates and system maintenance. This ensures that your applications and data are running on the latest software versions with the most up-to-date security patches. It also frees up IT teams to focus on more strategic tasks rather than routine maintenance.
- Disaster Recovery
Cloud computing offers robust disaster recovery solutions. With automated backup and replication features, businesses can recover data and applications swiftly in the event of data loss or system failures. This provides peace of mind and minimizes downtime.
- Environmental Benefits
Using cloud services can also be environmentally responsible. By sharing infrastructure with other users, cloud providers can achieve higher utilization rates, which can lead to energy and resource savings compared to traditional data centers.
- Global Reach
Cloud providers have data centers strategically located around the world. This global reach enables businesses to expand their services and reach new markets without the need to set up physical infrastructure in each location.
- Innovation Acceleration
Cloud computing democratizes access to cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics. These services are readily available through cloud platforms, allowing businesses of all sizes to harness the power of innovation without the need for extensive in-house expertise.
Use Cases of Cloud Computing
The advantages of cloud computing have enabled a wide range of use cases across various industries. Here are some examples:
- E-commerce: Online retailers leverage cloud computing to handle peak traffic loads during sales events, ensuring seamless customer experiences.
- Healthcare: Healthcare providers store and manage patient records securely in the cloud, facilitating data sharing among medical professionals and researchers.
- Finance: Financial institutions use the cloud for risk analysis, fraud detection, and secure customer data storage.
- Media and Entertainment: Streaming platforms rely on the cloud to deliver content globally, allowing users to access their favorite movies and shows on-demand.
- Education: Educational institutions use cloud-based platforms for remote learning, making education accessible to students worldwide.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturers employ cloud-based systems for supply chain management, predictive maintenance, and quality control.
- Gaming: Cloud gaming services offer high-quality gaming experiences without the need for expensive gaming consoles or hardware.
Challenges and Considerations
While cloud computing offers numerous advantages, it's essential to consider potential challenges and factors to make informed decisions:
- Security and Privacy: While cloud providers implement robust security measures, the responsibility for data security also lies with the user. It's crucial to understand the shared responsibility model and implement appropriate security measures.
- Data Transfer Costs: Moving large volumes of data to and from the cloud can incur significant costs, especially if your internet connection has limited bandwidth.
- Compliance and Legal Considerations: Some industries have strict regulatory requirements regarding data storage and processing. Ensure your chosen cloud provider complies with relevant regulations.
- Vendor Lock-In: Migrating data and applications from one cloud provider to another can be challenging and costly. Consider strategies to mitigate vendor lock-in.
- Downtime: While cloud providers strive for high uptime, no service is entirely immune to outages. Plan for downtime and implement backup strategies.
Cloud computing has transformed the way individuals and businesses operate in the digital age. Its advantages, including cost-efficiency, scalability, accessibility, and security, have made it an integral part of our technology landscape.
Cloud computing not only offers immediate benefits but also serves as an enabler for innovation and growth. As we continue to embrace the cloud, it's essential to remain informed about best practices, security measures, and evolving technologies to harness its full potential while mitigating associated challenges.
What's Your Reaction?