The Role of Vacuum Casting in the Automotive Industry
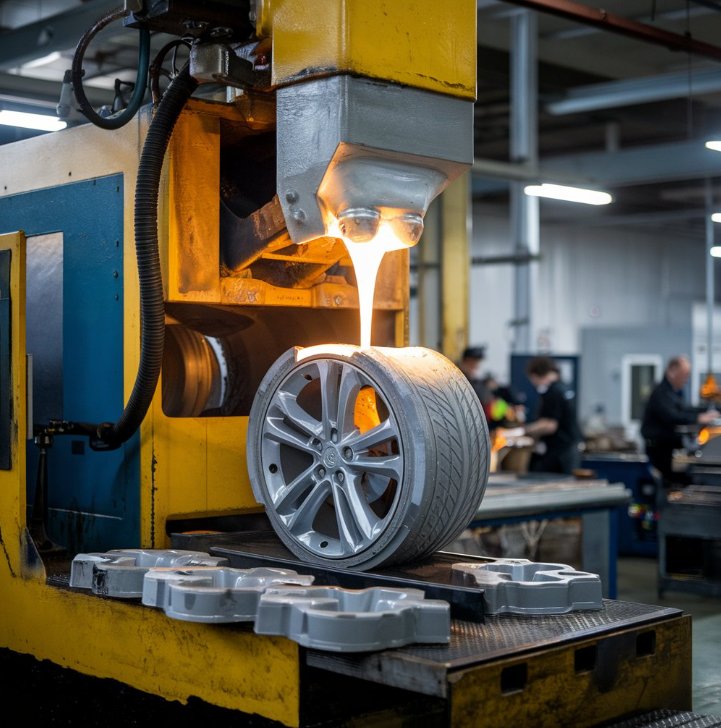

The automotive industry is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the demand for efficient, high-quality manufacturing processes. One such process that has gained prominence is vacuum casting. Known for its precision and versatility, vacuum casting plays a pivotal role in producing high-quality components, prototypes, and parts for the automotive sector.
In this article, we’ll explore what vacuum casting is, how it works, and its applications and benefits in the automotive industry.
What is Vacuum Casting?
Vacuum casting is a manufacturing process used to create high-quality prototypes and low-volume production parts. It involves pouring liquid materials (such as polyurethane resin) into a silicone mold under vacuum conditions. This ensures the material fills every intricate detail of the mold, resulting in precise and defect-free components.
How Does Vacuum Casting Work?
The vacuum casting process typically includes the following steps:
- Master Model Creation: A master model is produced, often using 3D printing or CNC machining. This model serves as the blueprint for the silicone mold.
- Mold Creation: A silicone mold is created by pouring silicone around the master model and allowing it to cure. Once cured, the mold is cut to release the master model.
- Casting Under Vacuum: Liquid resin is poured into the mold under vacuum conditions to eliminate air bubbles and ensure the material fills all mold cavities.
- Curing: The cast part is left to cure inside the mold before being removed.
- Finishing: The final part may undergo finishing processes such as sanding, painting, or coating.
Applications of Vacuum Casting in the Automotive Industry
Vacuum casting is widely used across various stages of automotive manufacturing, from prototyping to small-scale production. Here are its key applications:
Prototyping
Vacuum casting is ideal for creating precise and functional prototypes of automotive components. These prototypes are used for:
- Design Validation: Testing the fit, form, and function of components.
- Performance Testing: Evaluating mechanical properties under real-world conditions.
- Aesthetic Review: Assessing the look and feel of parts before full-scale production.
Low-Volume Production
For small batch production, vacuum casting offers a cost-effective alternative to injection molding. It’s often used for:
- Custom Components: Producing unique parts for high-end or specialty vehicles.
- Replacement Parts: Manufacturing parts for vintage or discontinued models.
Complex Component Manufacturing
Vacuum casting is particularly effective for creating components with intricate designs and fine details, such as:
- Dashboard panels
- Gear knobs
- Light casings
Functional Testing
Vacuum casting produces parts with properties that closely resemble production-grade materials. This makes it suitable for:
- Crash Testing: Evaluating the durability and safety of parts.
- Thermal Testing: Testing heat resistance for components like engine covers.
Advantages of Vacuum Casting in the Automotive Industry
1. High Precision and Detail
The vacuum casting process ensures that every intricate feature of the mold is captured, resulting in highly accurate components. This is crucial for parts that require tight tolerances and aesthetic precision.
2. Material Versatility
Vacuum casting supports a wide range of materials, including resins that mimic production-grade plastics, rubbers, and even some metal alloys. This allows manufacturers to produce components with specific properties such as:
- High impact resistance
- Flexibility
- Heat resistance
3. Cost-Effective for Small Batches
Unlike injection molding, which requires expensive tooling, vacuum casting is more affordable for low-volume production. The silicone molds are less costly to create and can be reused multiple times.
4. Quick Turnaround
The process of vacuum casting is relatively fast, making it ideal for industries like automotive where rapid prototyping and production are essential.
5. Low Waste and Eco-Friendly
Vacuum casting generates minimal material waste, as the process is highly efficient. This aligns with the automotive industry’s push for sustainable manufacturing practices.
Challenges of Vacuum Casting
While vacuum casting offers many advantages, there are some limitations to consider:
- Limited to Small Batches: The silicone molds degrade over time, making vacuum casting less suitable for mass production.
- Material Restrictions: Not all materials used in large-scale production are compatible with vacuum casting.
- Manual Steps: Some aspects of the process, like mold preparation and part removal, are labor-intensive.
Future of Vacuum Casting in the Automotive Industry
As automotive manufacturers continue to innovate, the role of vacuum casting is expected to expand. Emerging trends include:
- Integration with 3D Printing: Combining vacuum casting with additive manufacturing to create hybrid production workflows.
- Advanced Materials: Development of new casting resins with enhanced mechanical and thermal properties.
- Automation: Streamlining manual steps in the process to improve efficiency and scalability.
Conclusion
Vacuum casting is a versatile and reliable manufacturing process that plays a vital role in the automotive industry. From creating precise prototypes to producing low-volume components, it offers manufacturers the flexibility, efficiency, and quality needed to innovate and compete in a fast-paced market.
With advancements in materials and automation, vacuum casting is poised to remain a valuable tool for the automotive industry, driving innovation and supporting the creation of vehicles that are both functional and aesthetically superior.
What's Your Reaction?